
In welchem Alter sollte eine kieferorthopädische Behandlung bei Kindern beginnen?
Orthodontic treatment in children should generally begin between the ages of 6 and 12; early diagnosis is important.
The question of at what age should children begin orthodontic treatment is one of the most frequently asked questions by parents. Because dentists often give varying answers about the optimal age for orthodontic treatment, they may be unsure when to begin treatment.
Children's first orthodontic examination should be performed between the ages of 7 and 9, and checkups can be delayed until the age of 11 or 12 at the latest to determine if there are any dental or jaw problems. While there is no age limit for orthodontic treatment, early treatment planning, considering jaw development and tooth growth, can prevent future problems.
The importance of the question of at what age should children begin orthodontic treatment can be explained as follows. If orthodontic treatment is initiated during the growth and developmental period rather than postponed until adulthood, treatment will progress more easily and quickly, and more effective results can be achieved. If children exhibit habits such as mouth breathing, thumb sucking, abnormally protruding or receding upper and lower jaws, crossbite, or excessive crowding, they should be taken to an orthodontist for a detailed examination. Let's take a closer look at the age at which children should begin orthodontic treatment, and what the age limit is.
What Methods Are Used in Children's Orthodontic Treatment? Pediatric Orthodontic Treatment Applications
There are many methods used in children's orthodontic treatment. The primary goal of children's orthodontic treatment is to eliminate the problem. The first method to be applied is to seek help from a specialist who is knowledgeable about the cause of the problem. For example, for respiratory problems, support can be sought from an ENT specialist. Therefore, treatment approaches for each problem must be different.
Two types of appliances are used during children's orthodontic treatment: intraoral and extraoral appliances. There are two types of intraoral appliances: removable palatal appliances and fixed brackets. Removable braces are used for narrow jaws and as space maintainers, while braces are used for treatments such as closing gaps and adjusting the angle of teeth. Fixed braces are bonded to the teeth with a special adhesive and are not removed during treatment. Their advantage is that they accelerate tooth movement and allow for quick placement.
For pediatric orthodontic treatment, extraoral appliances are generally used to correct skeletal problems or to support intraoral appliances. Extraoral appliances, such as neck braces and headgear, are worn for approximately 18 hours a day, providing both orthodontic and orthopedic benefits. The pediatric orthodontist will determine the appropriate treatment.
If the optimal age for orthodontic treatment is not exceeded, the results will be faster. You can obtain information about orthodontic treatment age limits from our dentists.
What Are the Results of Pediatric Orthodontic Treatment?
The goal of pediatric orthodontic treatment is to prevent future problems and ensure healthy tooth growth. Orthodontic problems can be largely prevented by taking precautions at an early age.
Pediatric orthodontic treatment prevents bone and dental problems caused by bad habits such as thumb sucking, prolonged bottle or pacifier use, tongue thrusting, and mouth breathing. It creates room for narrow and receding upper jawbones. It helps your child's jaw and teeth grow in a healthy and aligned position, improves their physical appearance, boosts their self-confidence, prevents upper respiratory tract disorders, prevents trauma from misaligned upper front teeth, and prevents tooth fractures and loss.
Related Blogs
-
 What is a Prosthetic Tooth? How is it Attached?
What is a Prosthetic Tooth? How is it Attached? -
What is Restorative Dentistry?
-
Clear Braces
-
 Transparent Plaque Treatment
Transparent Plaque Treatment -
What to Do in Case of Severe Toothache Problems
-
Recommendations for Those Who Use Dentures
-
 Radio Orthodontics
Radio Orthodontics -
 What is Leaf Porcelain?
What is Leaf Porcelain? -
Cleft Lip
-
Symptoms of Wisdom Tooth Pain
-
 What is a Prosthetic Tooth? How is it Attached?
What is a Prosthetic Tooth? How is it Attached? -
 5 Great Tips for a Trouble-Free First Day of Orthodontic Treatment
5 Great Tips for a Trouble-Free First Day of Orthodontic Treatment -
 How to Put on Braces?
How to Put on Braces? -
 Do Braces Affect Speech?
Do Braces Affect Speech? -
Why Are Teeth Crooked (Twisted)?
-
 Who Are Corrective Orthodontic Treatments Applied To?
Who Are Corrective Orthodontic Treatments Applied To? -
 Gapped Teeth (Diastema) Treatment
Gapped Teeth (Diastema) Treatment -
 Do I Need to Use Retainers or Wires After Braces?
Do I Need to Use Retainers or Wires After Braces? -
 What Braces Colors Are Available? Which One Is Best For You?
What Braces Colors Are Available? Which One Is Best For You? -
 How to Floss With Braces?
How to Floss With Braces? -
Do Braces Cause Cavities?
-
What Should You Do If Your Bracket Gets Sinked or Broken?
-
Crooked Teeth Treatment
-
Palate Treatment
-
Fear of the Dentist in Children
-
 In welchem Alter sollte eine kieferorthopädische Behandlung bei Kindern beginnen?
In welchem Alter sollte eine kieferorthopädische Behandlung bei Kindern beginnen? -
What is Clear Correct Clear Aligner Treatment?
-
 Jaw Anomalies
Jaw Anomalies -
Extraoral Appliances in Orthodontics
-
 What is the difference between Invisalign Transparent Plate Treatment and others?
What is the difference between Invisalign Transparent Plate Treatment and others? -
 Antalya Lara Dental Clinic
Antalya Lara Dental Clinic -
 Antalya Muratpaşa Dental Clinics
Antalya Muratpaşa Dental Clinics -
 Antalya Dentist
Antalya Dentist -
 What is a Tooth Abscess? How to Treat It?
What is a Tooth Abscess? How to Treat It? -
 What is Cracked Tooth Syndrome?
What is Cracked Tooth Syndrome? -
Wisdom Teeth Symptoms and Surgery
-
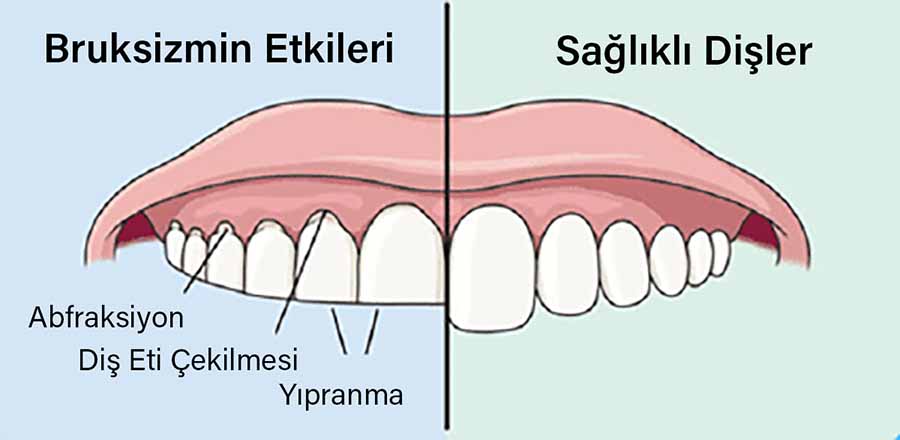 What is Bruxism?
What is Bruxism? -
 What Causes Dry Mouth?
What Causes Dry Mouth? -
 What is Restorative Dentistry?
What is Restorative Dentistry? -
 Why Does the Tooth with Root Canal Treatment Hurt ?
Why Does the Tooth with Root Canal Treatment Hurt ? -
 What is Fluoride?
What is Fluoride? -
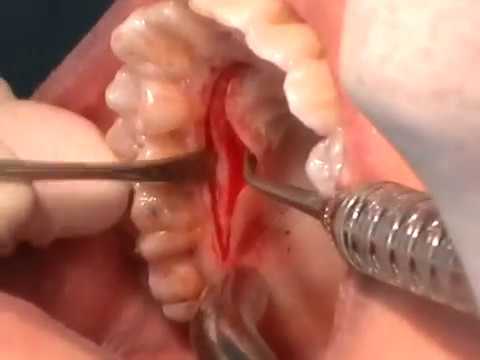 Taking Flesh from the Palate and Making Gums
Taking Flesh from the Palate and Making Gums -
 When Do Milk Teeth Fall Out?
When Do Milk Teeth Fall Out? -
 What type of mirror is a dentist's mirror?
What type of mirror is a dentist's mirror? -
 How to Treat Swollen Gum?
How to Treat Swollen Gum? -
 What Causes Toothache?
What Causes Toothache? -
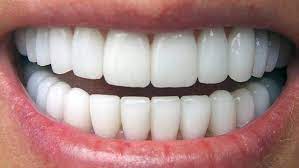 How is Dental Veneer Made?
How is Dental Veneer Made? -
 Teeth Models According to Face Shape
Teeth Models According to Face Shape -
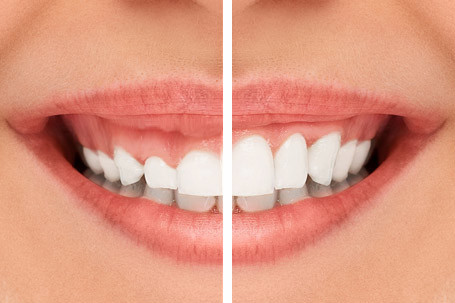 What is Good for Receding Gums?
What is Good for Receding Gums? -
 Removable Prosthesis Types
Removable Prosthesis Types -
 Types of Dental Veneers
Types of Dental Veneers -
 What Happens If the Root of a Broken Tooth Remains?
What Happens If the Root of a Broken Tooth Remains? -
 What Should Be Done to Whiten Yellowing Teeth?
What Should Be Done to Whiten Yellowing Teeth? -
 What is Aesthetic Filling
What is Aesthetic Filling -
 Ağzımı Açarken Çenemden Kemik Sesi Geliyor
Ağzımı Açarken Çenemden Kemik Sesi Geliyor -
 Debridman Nedir?
Debridman Nedir?
Related Blogs
-
 What is a Prosthetic Tooth? How is it Attached?
What is a Prosthetic Tooth? How is it Attached? -
What is Restorative Dentistry?
-
Clear Braces
-
 Transparent Plaque Treatment
Transparent Plaque Treatment -
What to Do in Case of Severe Toothache Problems
-
Recommendations for Those Who Use Dentures
-
 Radio Orthodontics
Radio Orthodontics -
 What is Leaf Porcelain?
What is Leaf Porcelain? -
Cleft Lip
-
Symptoms of Wisdom Tooth Pain
-
 What is a Prosthetic Tooth? How is it Attached?
What is a Prosthetic Tooth? How is it Attached? -
 5 Great Tips for a Trouble-Free First Day of Orthodontic Treatment
5 Great Tips for a Trouble-Free First Day of Orthodontic Treatment -
 How to Put on Braces?
How to Put on Braces? -
 Do Braces Affect Speech?
Do Braces Affect Speech? -
Why Are Teeth Crooked (Twisted)?
-
 Who Are Corrective Orthodontic Treatments Applied To?
Who Are Corrective Orthodontic Treatments Applied To? -
 Gapped Teeth (Diastema) Treatment
Gapped Teeth (Diastema) Treatment -
 Do I Need to Use Retainers or Wires After Braces?
Do I Need to Use Retainers or Wires After Braces? -
 What Braces Colors Are Available? Which One Is Best For You?
What Braces Colors Are Available? Which One Is Best For You? -
 How to Floss With Braces?
How to Floss With Braces? -
Do Braces Cause Cavities?
-
What Should You Do If Your Bracket Gets Sinked or Broken?
-
Crooked Teeth Treatment
-
Palate Treatment
-
Fear of the Dentist in Children
-
 In welchem Alter sollte eine kieferorthopädische Behandlung bei Kindern beginnen?
In welchem Alter sollte eine kieferorthopädische Behandlung bei Kindern beginnen? -
What is Clear Correct Clear Aligner Treatment?
-
 Jaw Anomalies
Jaw Anomalies -
Extraoral Appliances in Orthodontics
-
 What is the difference between Invisalign Transparent Plate Treatment and others?
What is the difference between Invisalign Transparent Plate Treatment and others? -
 Antalya Lara Dental Clinic
Antalya Lara Dental Clinic -
 Antalya Muratpaşa Dental Clinics
Antalya Muratpaşa Dental Clinics -
 Antalya Dentist
Antalya Dentist -
 What is a Tooth Abscess? How to Treat It?
What is a Tooth Abscess? How to Treat It? -
 What is Cracked Tooth Syndrome?
What is Cracked Tooth Syndrome? -
Wisdom Teeth Symptoms and Surgery
-
 What is Bruxism?
What is Bruxism? -
 What Causes Dry Mouth?
What Causes Dry Mouth? -
 What is Restorative Dentistry?
What is Restorative Dentistry? -
 Why Does the Tooth with Root Canal Treatment Hurt ?
Why Does the Tooth with Root Canal Treatment Hurt ? -
 What is Fluoride?
What is Fluoride? -
 Taking Flesh from the Palate and Making Gums
Taking Flesh from the Palate and Making Gums -
 When Do Milk Teeth Fall Out?
When Do Milk Teeth Fall Out? -
 What type of mirror is a dentist's mirror?
What type of mirror is a dentist's mirror? -
 How to Treat Swollen Gum?
How to Treat Swollen Gum? -
 What Causes Toothache?
What Causes Toothache? -
 How is Dental Veneer Made?
How is Dental Veneer Made? -
 Teeth Models According to Face Shape
Teeth Models According to Face Shape -
 What is Good for Receding Gums?
What is Good for Receding Gums? -
 Removable Prosthesis Types
Removable Prosthesis Types -
 Types of Dental Veneers
Types of Dental Veneers -
 What Happens If the Root of a Broken Tooth Remains?
What Happens If the Root of a Broken Tooth Remains? -
 What Should Be Done to Whiten Yellowing Teeth?
What Should Be Done to Whiten Yellowing Teeth? -
 What is Aesthetic Filling
What is Aesthetic Filling -
 Ağzımı Açarken Çenemden Kemik Sesi Geliyor
Ağzımı Açarken Çenemden Kemik Sesi Geliyor -
 Debridman Nedir?
Debridman Nedir?
Populer Blogs
-
 Uykuda Diş Gıcırdatma Neden Olur?
Uykuda Diş Gıcırdatma Neden Olur?





