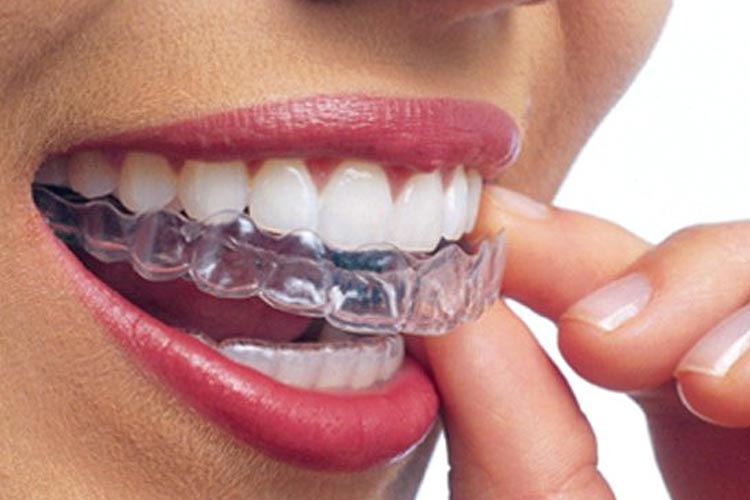
Gum Recession
Gum recession is the retraction of the gum tissue surrounding the teeth, exposing the tooth or tooth root. If gingival recession is not treated, the tissue and bone structures that support the teeth can be seriously damaged and tooth loss can occur.
When gingival recession occurs, both aesthetic and biological problems arise. Sometimes it can be caused by improper brushing, sometimes by clenching or grinding teeth, and sometimes by poorly made dental fillings or crowns. It usually occurs as a result of advanced gum disease and loss of underlying bone volume. Some important symptoms appear before the disease. Taking these symptoms into account, it is possible to stop the gingival recession problem, which is difficult to treat, before it progresses.
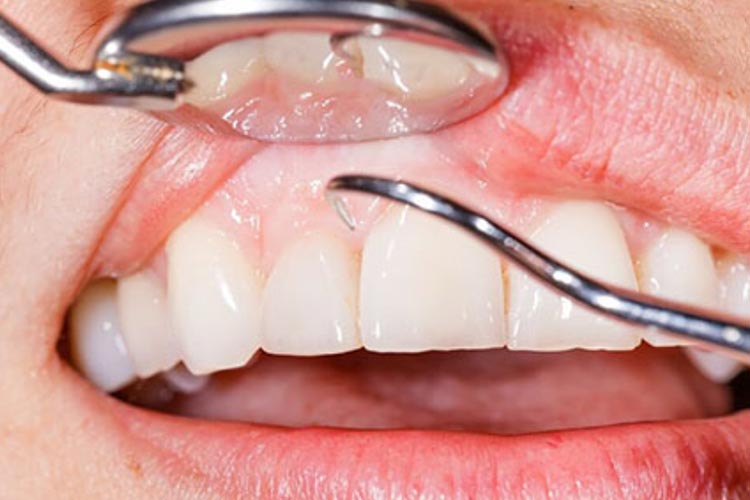
Gum Recession
Populer Services

The health and appearance of teeth are among the most important factors affecting daily life. While healthy and good-looking teeth are an advantage, there are certain procedures that must be performed to maintain this. In some cases, due to aging, inadequate care, or illness, teeth can be negatively affected. Specialist dentists are available to prevent this.
With a Denizli dentist, it is possible to solve any existing problem in the most appropriate way. The dentists in Denizli, part of the Tülay Akkol Private Oral and Dental Health Clinic, provide the most appropriate treatment for each patient. The hospital, one of Denizli's private dental hospitals, offers treatment focused on teeth and the mouth. Denizli Dental Hospital can solve many dental and oral problems and improve existing conditions. Dentistry is not always chosen for treatment, but sometimes for aesthetic purposes.
Aesthetics are not always applied to the face, and the appearance of the mouth and teeth is also affected by this. Therefore, many specialist Denizli dentists also practice aesthetic dentistry. Denizli offers a wide range of oral and dental services, including services for those visiting Denizli and surrounding provinces. Denizli dentists operate with a patient-centered approach to deliver the best results with their specialized services. Denizli also has an emergency dental hospital.
Denizli Dentist Services
Tülin Akkol Private Oral and Dental Health Clinic is among Denizli's dental clinics and offers a wide range of services. It's advantageous to divide Denizli dental services into two main categories: cosmetic dentistry and health-focused dentistry performed for surgical purposes. Health-focused surgical dentistry, in particular, encompasses a wide range of services. It can also be combined with certain cosmetic dentistry procedures.
Pedodontics: This group of procedures covers children between the ages of 0 and 13, focusing specifically on children's dental development and potential health problems. A specialist Denizli dentist who performs pedodontics can address children's dental problems. Denizli pediatric dentistry services are not available for those aged 13 and over.
Anesthesia Applications: This procedure is performed to minimize discomfort for patients during many procedures. Anesthesia can be used for many serious procedures. This eliminates pain and allows for more comfortable procedures. It can be used for many other procedures, such as wisdom tooth extraction and dentures.
Filling Applications: A general term for fillings, also known as root canal treatment, is used in Denizli dental clinics as an additional procedure after the decayed portion of the tooth has been removed. The Denizli dentist will select the highest quality and most appropriate material for the procedure, which is available in a variety of materials.
Surgical Procedures: Surgical procedures include a wide variety of procedures. The hospital, which is staffed by Denizli's top dentists and staff, is considered the most definitive procedure. It is preferred in serious and intensive cases. When necessary, periodontal treatment can also be performed by Denizli's top dentists and team. It is also used in procedures such as wisdom tooth surgery.
Implant Applications: It's possible to replace missing teeth for a variety of reasons and restore your former, high-quality smile. Denizli implants aim to achieve the most natural dental appearance. Denizli's top dentist and expert team perform implant applications with the most accurate method and the most suitable materials, ensuring a healthy mouth.
Orthodontic Applications: Tülay Akkol Private Oral and Dental Health Clinic provides orthodontic services in Denizli. This procedure, which is preferred for both surgical and aesthetic purposes, allows for correcting misaligned teeth. Denizli orthodontists are experienced in this field and provide the most appropriate shape for the mouth.
Denizli Cosmetic Dentistry
Cosmetic dentistry in Denizli utilizes technological advancements and equipment. An aesthetic perspective is also essential. These procedures performed at the Oral and Dental Health Clinic require a digital smile design first. After an image of the mouth is taken, the necessary procedures are determined. Our specialists in cosmetic dentistry are also involved in the planned procedures, taking your wishes into account. The cosmetic dentist determines the treatment needs of the patient. The process then proceeds according to the patient's preference. While some aesthetic interventions are mandatory, others Hide More

Our philosophy is to offer treatment to all people by focusing on the relationship of your teeth and gums to your total body health. We want you to make sure that your smile reaches your goals for comfort, function and appearance. We are here to do this. We also understand that the choice of dentist is an important decision. After all, your smile says a lot about your greatest asset and overall health. You will be greeted in an environment where you can relax from the moment you enter the door.
- +90 (258) 262 30 52
- contact@tulayakkol.com.tr